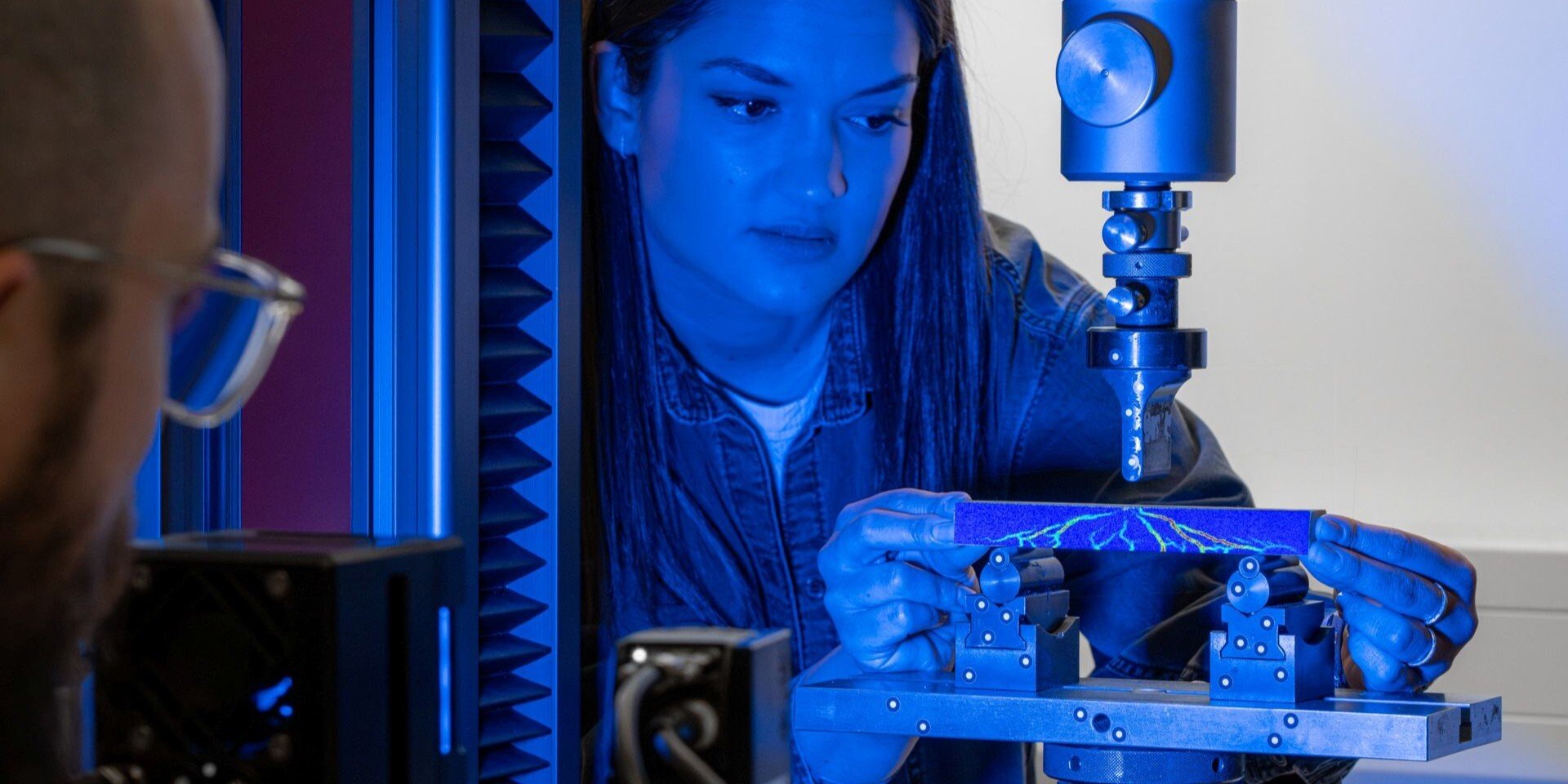
Phone Drop Test
We had a "smashing" time with this phone drop test! During this test, we used the ARAMIS optical testing system to measure the major strain as the...

15:36, Feb 24
15:19, Feb 19
2 min read
Charles-Olivier Amyot
:
January 4, 2023 5:06:24 PM EST
In the battery industry, precise measurement is critical for ensuring high-quality products that meet strict specifications. Traditional measurement techniques such as calipers or gauges can be time-consuming and prone to human error, making it difficult to achieve the level of accuracy required in the industry.
This is where Digital Image Correlation (DIC) comes in. DIC is a non-contact, optical measurement technique that uses digital images to measure the deformation of an object under load. By analyzing the displacement of a pattern on the surface of the object, DIC can accurately measure the dimensions and shape of the pouch with a high degree of accuracy.
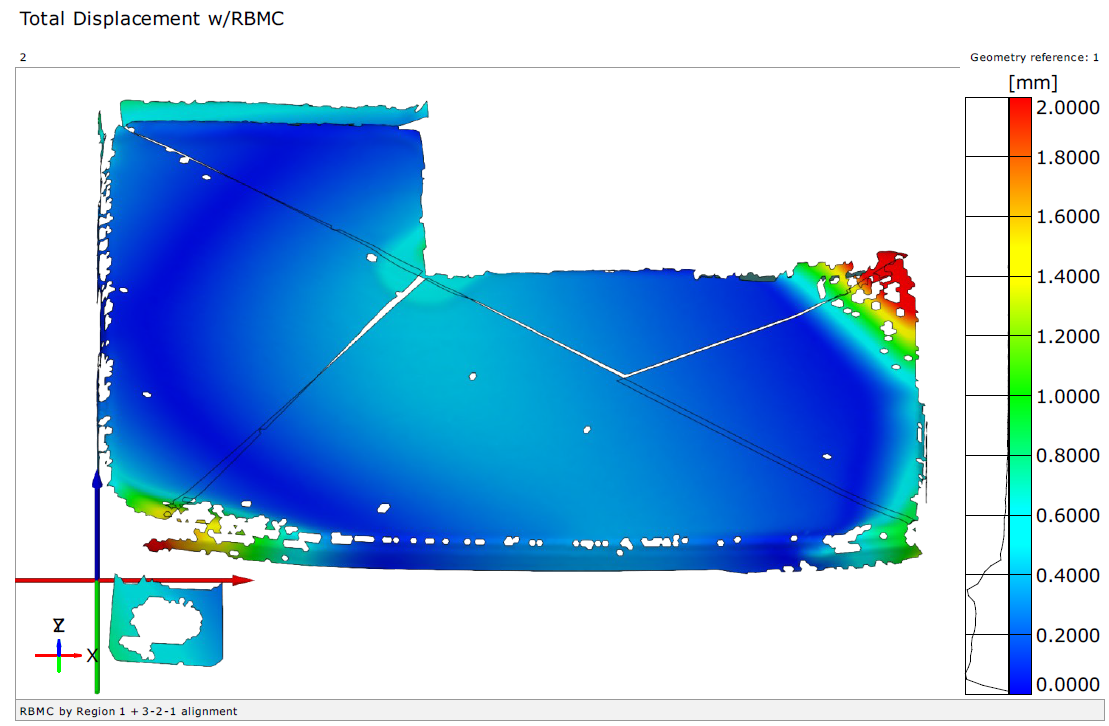
We recently developed a test methodology using DIC for measuring batteries of small electronic devices. This method involves using an ARAMIS system to perform the DIC measurements and a GOM Rotating Table to automate various views of the battery. All these views and smaller projects are then added to a main project. Once all the images are added to this main project, they are oriented together with a separate stage transformation using uncoded markers on the table. This allows for the creation of a single project that stitched together using a nominal point, giving an ARGUS-like result in an ATOS-like scan measurement.
One of the main benefits of this hybrid test methodology is its speed and efficiency. Traditional measurement techniques can be slow and labor-intensive, requiring multiple measurements to be taken and averaged to get an accurate result. DIC, on the other hand, can quickly and accurately measure the entire surface of the pouch in a single scan, saving time and improving productivity.
In addition to its speed, DIC offers a high level of accuracy. It is capable of measuring deformations as small as 0.1 microns, making it ideal for precise measurement applications. This level of accuracy is critical in the battery pouch industry, where even small deviations from specifications can have significant impacts on performance and reliability.
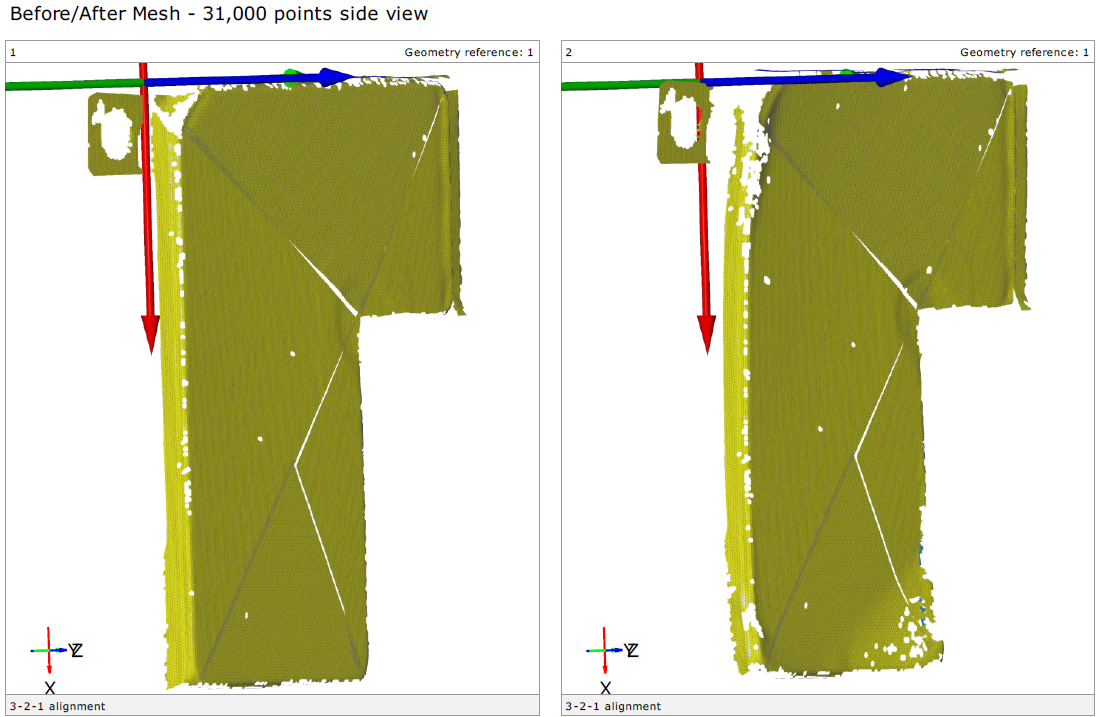
Overall, digital image correlation is a powerful tool for accurately and efficiently measuring batteries of all sizes. By using this test methodology, manufacturers can take advantage of the speed and accuracy of DIC to improve their quality control processes and ensure that their pouches meet the highest standards and not only get 3D scans and shape measurements, but also strain data and deformations of the film and general envelope of the batteries. This is critical for various battery designs, and as shown here with lithion-ion replacements, where the ability to accurately measure the battery performance response after a reliability test campaign for example might be essential for ensuring proper function and performance. Using our ARAMIS Optical Strain systems can help your company prevent catastrophic failure and avoid bad designs. Read more about how ARAMIS can replace strain gages and displacement sensors!
We had a "smashing" time with this phone drop test! During this test, we used the ARAMIS optical testing system to measure the major strain as the...
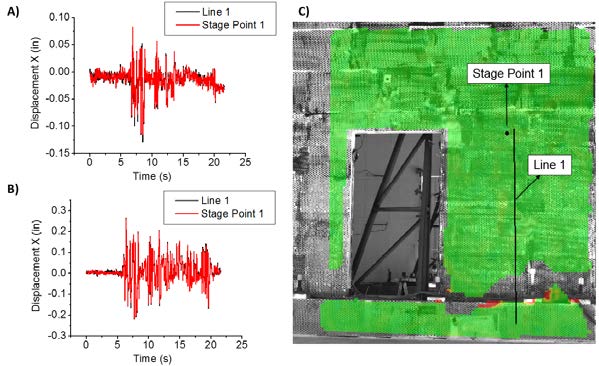
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT